Research activity oriented to fulfil the S&T objectives led to the following results:
- Process data were generated for grades Ti-40 and Ti 15-3-3-3. Process data included process parameters, tool paths and experimental practises.
- Process data were generated to hot form alloys of interest (i.e. Ti 6Al-4V).
- Cold Spinnability data were generated for grades Ti-40, Ti 15-3-3-3 and Ti 6Al-4V.
- Specific rolling tools were designed, fabricated and tested for both cold and hot forming operations.
- FE process models were implemented and validated to simulate cold forming of Ti-40 and hot forming of Ti 6Al-4V.
- Numerical computation techniques were tested to upscale the FE process models to real conditions (large scale parts, long tool paths).
- A specific material formability test was designed and formability data were obtained for Ti-40 and Ti 15-3-3-3.
- Post-forming material properties were tested and analysed for all cold and hot formed grades/alloys including metallographic analysis, static tensile testing and microhardness measurements.
- A classifier algorithm that predicts the geometric deviation of parts due to material springback was programmed and trained.
- An intelligent process model that using the classifier algorithm prediction provides a corrected tool path was implemented and validated.
- Heating means to heat up locally or globally Ti 6Al-4V along a hot forming operation were implemented and compared against each other.
Based on the technology basis implemented demonstrator parts were fabricated and their quality evaluated aiming to assess the potential of the AISF technology for the intended target of fabricating aircraft parts.
A strut half made of Inconel 718 was produced by cold forming to assess the feasibility to fabricate parts made of Ni-base alloys and two generic shapes of Ti 6Al-4V including design features typical of pylon fairings were made using hot dieless in order to assess the geometric accuracy attainable by the process.
The assessment of the demonstrators reported promising results in terms of surface quality and thickness distribution. Even significant improvement in the geometric accuracy of parts was observed compared to state-of-the-art practices.

Engine strut half

Airframe generic shape with features from pylon fairings
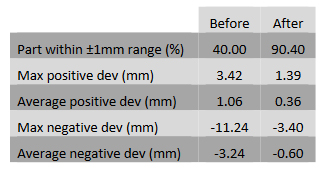
Geometric accuracy values before (left) and after (right) the hot dieless approach implemented for Ti 6Al-4V.
It can be said that though the implemented AISF-based technology requests from further technological developments yet, the generated results point out a significant step forward towards the industrialization of the technology for aircraft applications and, most likely, for applications from other sectors as well.
