ENCOMB: Project overview
Short summary
Driven by central problems within the aeronautics industry, which were thoroughly represented in the project by the industrial partners in AIRBUS Group, the ENCOMB project aimed to provide advanced non-destructive testing methods for reliable quality assurance of adhesive bonds of CFRP structural components.
The project brought together fourteen partners from ten European countries to examine extended NDT (ENDT) techniques for the characterization of adhered surfaces and adhesive bonds, towards introducing quality assurance concepts and enabling in-line and in-service quality control.
Five applications scenarios and respective ENDT requirements were identified of being of primary importance for the aircraft manufacturers:
- Hydraulic fluid/water contamination
- Release agent contamination
- Moisture contamination
- Thermal damage
- Weak bonds due to poorly cured adhesives
Adherend surfaces were characterised with conventional laboratory analysis methods (spectroscopic and optical techniques, contact angle measurements), in order to analyse their physicochemical properties resulting from sample preparation. In a similar way, adhesively bonded samples were characterised with conventional NDT techniques (ultrasonic and x-ray inspection, µ-CT), in order to analyse their structural integrity resulting from sample preparation.
Advanced NDT technologies for the detection of the selected physico-chemical properties of CFRP adherend surfaces and the quality of the adhesive bonds were identified, verified, developed, adapted, and validated for their potential to comply with the defined application scenarios and requirements.
In the end, advanced non-destructive testing (NDT) methods for pre- and post-bond inspection of CFRP aircraft structural components required to establish a reliable quality assurance concept for adhesive bonding were provided. State-of-the-art NDT techniques were screened and the most suitable ones were further developed and adapted to the application scenarios, with regard to aircraft manufacturing and in-service repair.
The project was officially launched on November, 2010 and was successful finished on April, 2014, completing its expected 42-month duration and its 20 scheduled deliverables.
The ENCOMB project has received funding from the European Union‘s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under grant agreement No 266226.
Impact
In order to extend the use of adhesive bonding for load-critical CFRP primary aircraft structures quality assurance processes for ensuring the performance of the adhesive joints have to be developed. The ENCOMB project has targeted this objective by identifying, screening, developing, and adapting NDT methods for the characterization of CFRP bonded structures, the characterization of the CFRP adherend surface state before bonding and the state of the cured and uncured adhesive.
Within the project major innovations with a strong impact on future manufacturing and repair of aircraft structures have been achieved, namely:
- Analytical techniques for characterizing adhered surfaces and for the assessment of the quality of adhesive bonds
- Knowledge about the effect of different contaminations on the adhesion properties and the overall bond performance according to the selected application scenarios
- Algorithm(s) that will provide bonding guidelines
- Quality assurance concept(s) for adhesive bonding of primary structures in aircraft manufacturing and in-service environment
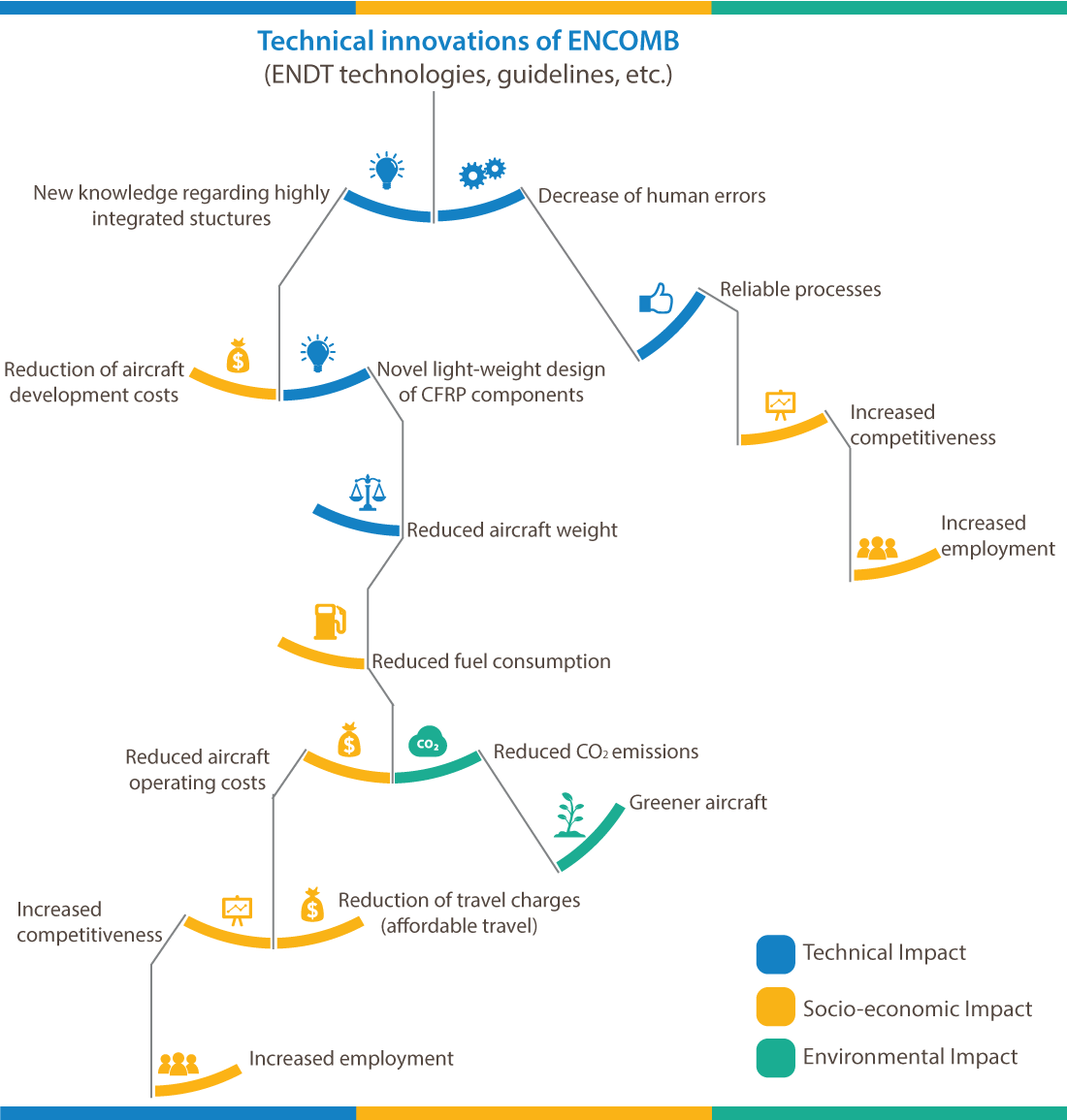
Fostered by the development of robust and reliable adhesive bonding processes, as well as the related quality assurance techniques, the increased use of advanced light-weight composite materials reinforces the competitiveness of Europe’s aircraft industry and European aircraft operators and thus employment is secured or even increased.
The project results will contribute to conserving and further expanding the European aeronautics industry, by generating added product value for aircraft manufacturers and reduced costs for operators.
On a socio-economic level, the achieved innovations will contribute to a reduction of fuel consumption which is directly connected to the operational cost of an aircraft leading to more affordable air transportation.
Lower fuel consumption has further significant ecological and societal benefits through reduced emission of CO2 and other toxic gases. Beside the ecological issue, there are societal demands for the reduction of energy consumption in transport and a higher ecological awareness from citizens and governments on the effect that uncontrolled growth can have on the environment.
Aeronautics stakeholders have proactively complied with these demands by establishing roadmaps providing perspectives for the greening of air transport. The Advisory Council for Aeronautics Research in Europe (ACARE) has elaborated a strategic research agenda listing ambitious goals for the Aeronautic Industry in Europe. One of them is a 50% reduction of CO2 emissions per passenger/km, i.e. a halving of the fuel burnt (based on the status in the year 2000). Just recently, even more ambitious goals have been elaborated by the High Level Group on Aviation Research and published by the European Commission in "Flightpath 2050 –Europe’s Vision for Aviation", which aims even for a 75% reduction of CO2 emissions (with the same baseline in the year 2000) by the year 2050.
The results of this project, in particular the novel ENDT technologies, quality assurance processes and the scientific progress regarding adhesive bonding, directly facilitate the implementation of adhesive bonding processes for highly integrated CFRP structures.
The expected weight savings for the fuselage airframe are up to 15%. These weight savings have further effects on the size and weight of the engines. This represents an important contribution towards the greening of European air transport.
Outside the civil aircraft sector, the implementation of ENDT technologies will be a promoter for new applications in different European industrial sectors that make use of fibre reinforced lightweight structures (e.g. transportation, wind energy industry). This can help other industries to improve their competitiveness and market share, a requirement for further employment increase in Europe.
Furthermore, the ENCOMB results hold the following technical impacts:
- Novel light-weight design of CFRP structural components, resulting from the obtained knowledge about assembly of highly integrated CFRP structures. If reliable bonding processes (by using ENDT technologies) are available, a huge increase of lightweight structural composite components is expected which is directly connected to weight savings
- A reduction of maintenance costs (e.g. by reducing the time for in-service repair), ensuring reliable (in-service) repair by adhesive bonding at the same time
- Reduced aircraft development costs, by the achieved knowledge and expertise regarding highly integrated structures with an optimum combination of advanced composite materials, eliminating and minimising the number of joins
- The decrease of human error during production, maintenance, and repair, which directly results in more reliable processes and increased safety of air transportation
The participation of major European aircraft manufacturer in the consortium makes the rapid acceptance and approval of the new developments and exploitation of project results for aeronautic applications very likely. Hence, it is expected that the project contributes significantly to the growth and competitiveness of the European aeronautic industry. It is worth mentioning that all consortium partners have spread information about the developed technologies between each other so as to ensure full exploitation. Interaction between consortium members enabled the exploitation of specific technologies through the leading industrial participants by incorporating new technologies into future products.
Based on the exploitation activities performed by the partners, two commercial exploitable foregrounds of R&D results and five general advancements of knowledge have been generated within the project.
Consortium Partners
Coordinated by Fraunhofer, ENCOMB brought together a multidisciplinary consortium of 14 partners from ten European countries, consisting of leading experts from top-level European research organizations, universities, and industries active in aeronautics research and development.
Altogether, four commercial companies participated in the project, three of them belonging to the major industrial players in the European aeronautics industry and a major manufacturer of electronic and analytical measurement instruments.
The upstream approach followed within this Level 1 project was reflected by the participation of recognised research organisations and universities. Furthermore, the participation of major European aircraft manufacturers ensured the relevance of the work through compliance with appropriate application scenarios, technological specifications and thus the greatest potential for the exploitation results.

Contact
EASN Technology Innovation Services BVBA
Terweidenstraat 28
B-3440 Budingen
Belgium
EASN Technology Innovation Services BVBA
Patras Science Park
Stadiou Str., Platani
26504, Patras, Greece
Tel: +30.2610.911378
EASN Technology Innovation Services BVBA
Ioanni Polemi 32A
3085, Limassol , Cyprus
Tel: +357.25212390
EASN Association
© 2024 EASN Technology Innovation Services · All rights reserved


